SNP Genotyping
GENEWIZ SNP Genotyping service is a PCR and Sanger sequencing-based solution that is used to ramp up SNP screening assays and validate SNPs of interest with speed and accuracy.
Genotyping is a method used to determine the genetic makeup of an organism. This method identifies genetic variations by comparing an individual’s sequence against a wild-type reference sequence to analyze single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). SNPs are present in both the coding and non-coding regions of a gene and are one of the most common types of variants; they are represented as a single nucleotide mutation within a DNA sequence.
SNP Genotyping
Genotyping is a method used to determine the genetic makeup of an organism. This method identifies genetic variations by comparing an individual’s sequence against a wild-type reference sequence to analyze single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). SNPs are present in both the coding and non-coding regions of a gene and are one of the most common types of variants; they are represented as a single nucleotide mutation within a DNA sequence.
GENEWIZ’s SNP Genotyping service is a PCR and Sanger sequencing-based solution that is used to ramp up SNP screening assays and validate SNPs of interest with speed and accuracy.
Request Quote

SNP Genotyping Analysis and Detection
SNP analysis and identification may help predict an individual’s response to certain drugs, susceptibility to environmental factors, and risk for developing diseases. Alternatively, SNPs can be used to track inheritance of disease genes within families and provide insight into SNP linkage.
Sanger sequencing-based SNP genotyping can be performed on a small subset of samples or as part of large-scale projects. Whether you are using genotyping as your primary approach for SNP analysis and detection, or to confirm next generation sequencing and microarray results, GENEWIZ from Azenta can help accelerate your project. Let the Sanger sequencing experts at GENEWIZ support your SNP genotyping research objectives with speed, quality, and reliability.
Service Highlights
| SNP GENOTYPING | |
| Starting Material | gDNA (extractions available) |
| Assay Coverage | Annotated SNPs of interest |
| Confirm | SNPs |
| Deliverables/Reports | Raw data files: .ab1, .seq |
| Nucleotide level mutations | |
*Customized reports available
Looking to identify non-annotated mutations in coding or non-coding regions of interest? See GENEWIZ Mutation Analysis service.
Features & Benefits
GENEWIZ SNP Genotyping WORKFLOW
1. PROJECT CONSULTATION & PRIMER DESIGN
Amplicon selection and primer design to targeted SNPs of interest
2. ASSAY DEVELOPMENT
Optimization of project-specific samples
3. PCR & PURIFICATION
PCR amplification of genomic DNA using optimized conditions
4. SEQUENCING & DATA ANALYSIS
Bi-directional DNA sequencing per amplicon and final report identifying SNPs
GENEWIZ vs. In-House
SNP Genotyping Turnaround Time Comparison: GENEWIZ versus In-house
GENEWIZ TURNAROUND: 3 DAYS
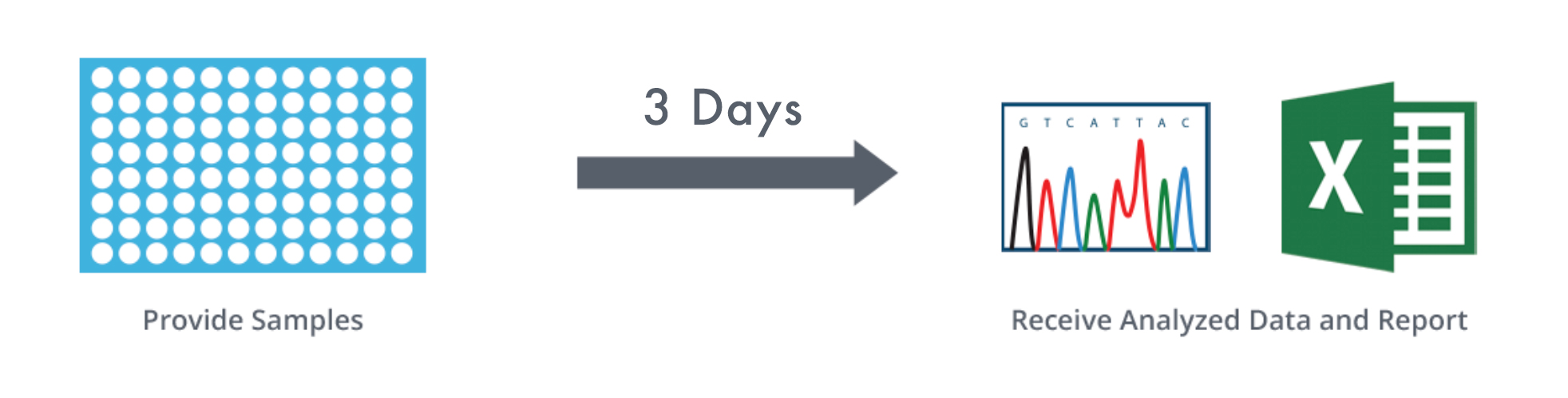
IN-HOUSE TURNAROUND: 2-4 WEEKS

Deliverables
All SNP Genotyping projects will receive a raw data file (Figure 1.) along with a final report identifying SNPs compared to the provided reference sequence (Figure 2.). Custom reports are also available upon request.
Example: BRAF c.1799T>A (V600E) Mutation in Melanoma
Mutations in BRAF are largely linked to malignant melanomas. Mutations at BRAF V600 are common indicators for responsiveness to treatment for melanoma patients.
Figure 1. Chromatogram
Chromatogram showing the heterozygous mutation at nucleotide position 1799 (T to A mutation at position 16 below) which correlates to amino acid position 600 (V to E mutation).
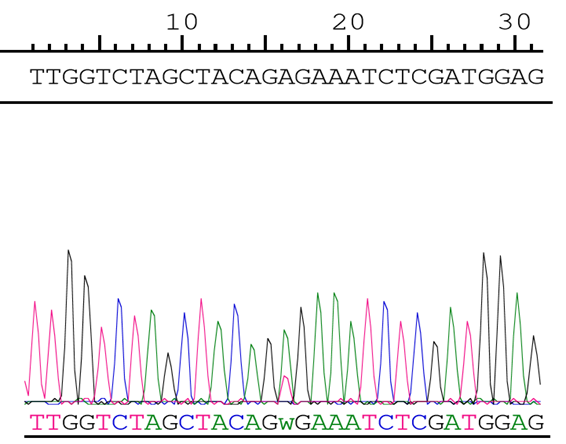
Figure 2. Final Report
A SNP genotyping final report shows the reference SNP ID number, the allelic mutation, and the flanking sequence with the highlighted position of the identified SNP.
| SNP ID | Alelles | Flanking Sequence | |
| rs113488022 | T/A | TTGGTCTAGCTACAGTGAAATCTCGATGGAG | |