Low-Pass Whole Genome Sequencing
Low-pass whole genome sequencing (also referred to as LP-WGS or shallow whole genome sequencing) is a cost-effective, high-throughput DNA sequencing technology used to detect genetic variation within the genomes of various species. Compared to genotyping arrays, this method is an affordable alternative for discovering new, rare variants with higher statistical power and increased data. LP-WGS helps to address questions related to statistical and population genetics, from complex-trait association studies to genome-wide polygenic risk score calculation.
What is low-pass whole genome sequencing?
Low-pass whole genome sequencing is a technique in which each base in the entire genome is sequenced a few times (known as low-depth coverage). On average, the depth of coverage is below 5 times and can be as low as 0.1-1 times.
By reducing the depth of coverage, the cost of sequencing the whole genome is reduced while maintaining a broad look at the full genome.
What is imputation in low-pass genome sequencing?
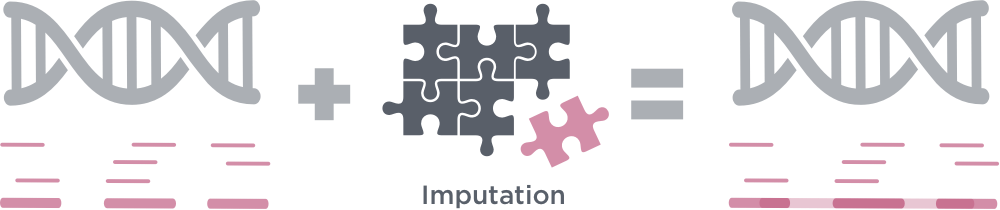
Imputation is the generation of sequencing data in parallel to reference data. In low-pass whole genome sequencing, imputation is important in accurately associating and evaluating genetic markers that are not directly sequenced.
LP-WGS relies on computational methods, called imputation, to fill in the missing information. Imputation algorithms allow up to 99% accurate variant call detection as compared to genotyping arrays. The unique combination of GENEWIZ LP-WGS and imputation enables scientists to efficiently obtain analysis-ready fully-imputed VCF files in a single service. For applications that require deep sequencing coverage of specific genomic regions or variants (i.e. clinical applications), GENEWIZ LP-WGS Plus combines LP-WGS with exome or targeted sequencing – the first of its kind on the market.
Low-Pass Whole Genome Sequencing Workflow
-

1. Experimental
Design -

2. Sample
Preparation -

3. Extraction
-
4. Library
Preparation -

5. Sequencing
0.1x -<10x -

6. Imputation
-
7. Variant
Calling
TECHNOLOGY SNAPSHOT: LOW-PASS WHOLE GENOME SEQUENCING
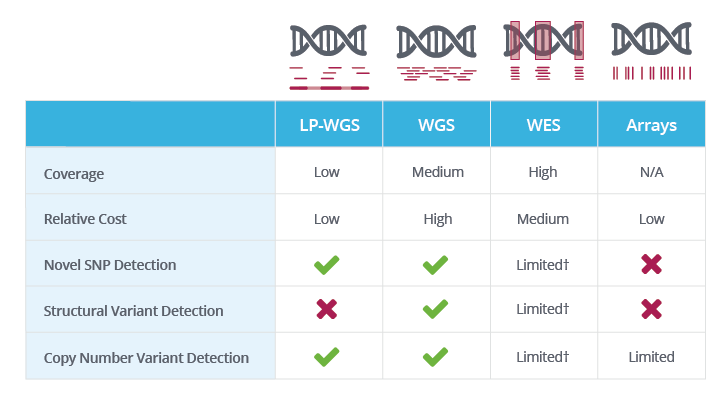
† WES coverage is limited to genic/exonic regions; hence, structural variants and copy number variants present only in these regions can be resolved.
DELIVERABLES
Standard Deliverables
- Sample QC (includes raw data QC & alignment metrics)
- FASTQ files
- Aligned BAM file
- Imputed VCF file
Human LP-WGS Deliverables
(In addition to standard deliverables)
- Copy number variant analysis
- Ancestry analysis
- Calculated polygenic risk scores files
Custom bioinformatics analysis and reports are available. Please contact us about how we can customize the analysis to answer your biological question.
LOW PASS WHOLE GENOME SEQUENCING PLUS





GENEWIZ LP-WGS Plus combines LP-WGS with exome or targeted sequencing – the first of its kind on the market.
FEATURES & BENEFITS
-

Superior Data Quality
Exceeding manufacturer’s benchmarks -

Real-Time Project Updates
Through our online system -

Ph.D.-Level Support
At every step
-
Highly accurate variant calls across the genome
-
10x more data than microarrays at 1/10th of the cost of standard WGS
-
High-throughput, cost-efficient and scalable
-
Low-Pass WGS Plus is a cost-effective solution for applications that require deep sequencing coverage of specific genomic regions or variants
-

PUBLICATION
Low-pass sequencing increases the power of GWAS and decreases measurement error of polygenic risk scores compared to genotyping arraysLearn how low-pass sequencing plus imputation, in addition to providing a substantial increase in statistical power for genome wide association studies, provides increased accuracy for polygenic risk prediction at effective coverages of ∼ 0.5x and higher.
-

PUBLICATION
Low-coverage sequencing cost-effectively detects known and novel variation in underrepresented populationIn this study, scientists from around the world (led by a group at the Broad Institute) considered specifically the question of association studies in African populations; these population are generally under-represented in existing genomics databases. They found that, depending on cost considerations and study goals, that low-pass sequencing in the range of 0.5x to 4x coverage outperformed a wide range of genotyping arrays.
-

WEBINAR
The $100 Genome: Using Low-Pass Whole Genome Sequencing as an Alternative to Genotyping ArraysIn this webinar originally presented at the ASHG 2020 Virtual Meeting, learn how low-pass WGS overcomes the inherent limitations and biases of traditional arrays, offering an inexpensive, high-throughput alternative for detecting genome-wide genetic variation and novel variants.
-

WORKSHOP
Workshop & Roundtable Discussion | Exploring Bioinformatics for Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) DataIn this recording of our WGS bioinformatics workshop & roundtable discussion led by bioinformatics scientist Zain Alvi, Ph.D., we’ll guide you through the WGS bioinformatics process to help you learn to interpret WGS bioinformatics results, as well as address common challenges and answer frequently asked questions (FAQs).
NGS PLATFORMS
For information on our NGS platforms as well as recommended configurations of your projects, please visit the NGS Platforms page. GENEWIZ from Azenta does not guarantee data output or quality for sequencing-only projects.